SpringMVC简介
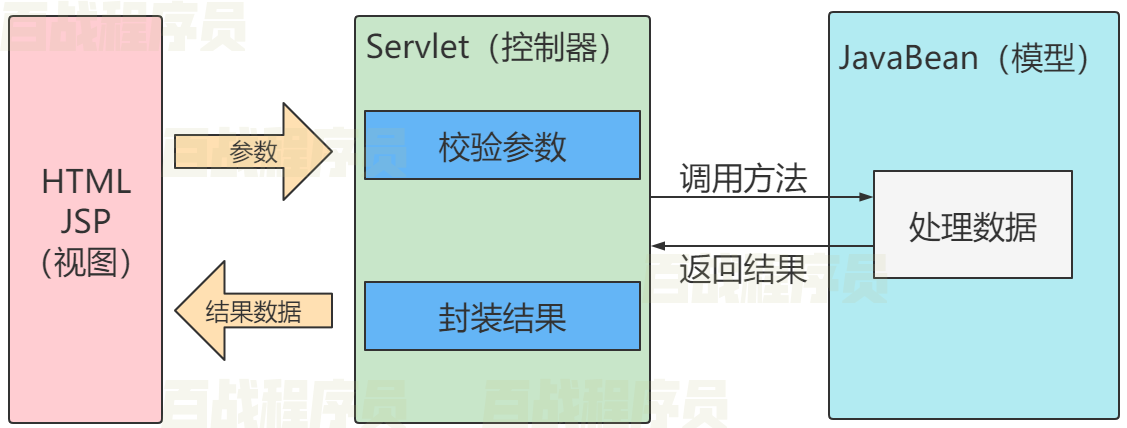
MVC模型
MVC全称Model View Controller,是一种设计创建Web应用程序的模式。这三个单词分别代表Web应用的三个部分:
Model(模型):指数据模型。用于存储数据以及处理用户请求的业务逻辑。在Web应用中,JavaBean对象、业务模型等都属于Model。
View(视图):用于展示模型中的数据的,一般为jsp或html文件
Controller(控制器):是应用程序中处理用户交互的部分,接受视图提出的请求,将数据交给模型处理,并将处理后的结果交给视图显示。
SpringMVC
SpringMVC是一个基于MVC模式的轻量级Web框架,是Spring框架的一个模块,和Spring可以直接整合使用。SpringMVC代替了Servlet技术,它通过一套注解,让一个简单的Java类成为处理请求的控制器,而无须实现任何接口。
(SpringMVC代替了S)
SpringMVC入门案例

接下来我们编写一个SpringMVC的入门案例
1.引入maven创建web项目,补齐包结构
2.引入相关依赖和tomcat插件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<artifactId>mvc_demo1</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>mvc_demo1 Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>8080</port>
<path>/</path>
<uriEncoding>UTF-8</uriEncoding>
<server>tomcat7</server>
<systemProperties>
<java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format>%1$tH:%1$tM:%1$tS %2$s%n%4$s: %5$s%6$s%n
</java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format>
</systemProperties>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
3.在web.xml中配置前端控制器DispathcerServlet
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
|
4.编写SpringMVC核心配置文件springmvc.xml,该文件和Spring配置文件写法一样
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan"></context:component-scan>
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
</beans>
|
5.编写控制器
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController1 {
@RequestMapping("/c1/hello1")
public void helloMVC()
{
System.out.println("hello SpringMVC!");
}
}
|
使用tomcat插件启动项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/c1/hello1
使用SpringMVC必须要配置的是前端控制器
SpringMVC执行流程
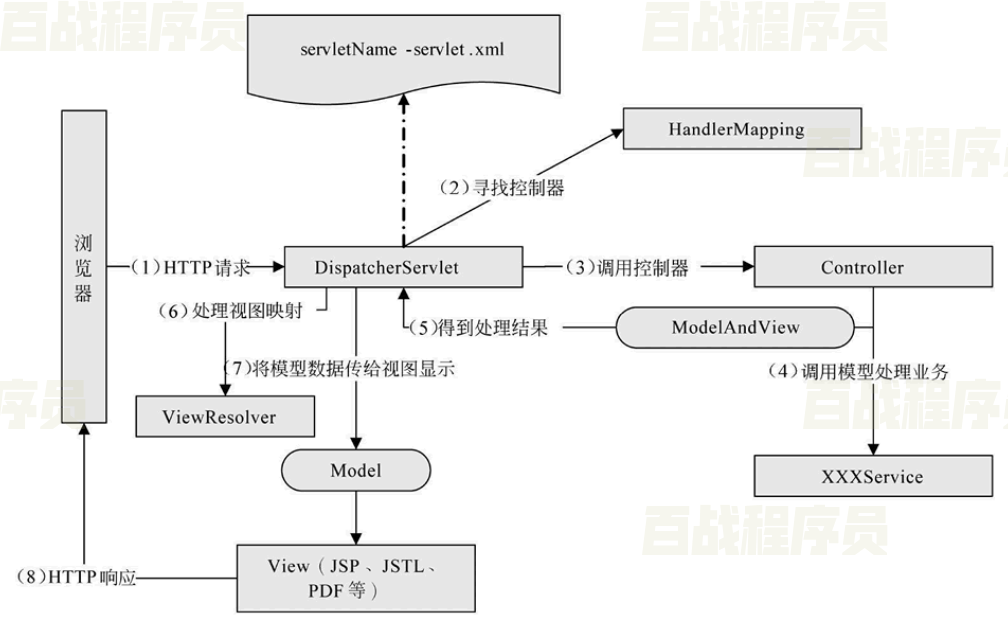
SpringMVC的组件:
- DispatcherServlet:前端控制器,接受所有请求,调用其他组件。
- HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,根据配置找到方法的执行链。
- HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,根据方法类型找到对应的处理器。
- ViewResolver:视图解析器,找到指定视图。
组件的工作流程
- 客户端将请求发送给前端控制器。
- 前端控制器将请求发送给处理器映射器,处理器映射器根据路径找到方法的执行链,返回给前端控制器。
- 前端控制器将方法的执行链发送给处理器适配器,处理器适配器根据方法类型找到对应的处理器。
- 处理器执行方法,将结果返回给前端控制器。
- 前端控制器将结果发送给视图解析器,视图解析器找到视图文件位置。
- 视图渲染数据并将结果显示到客户端
SpringMVC参数获取_封装为简单数据类型

在Servlet中我们通过request.getParameter(name)获取请求参数。该方式存在两个问题:
而SpringMVC支持参数注入的方式用于获取请求数据,即将请求参数直接封装到方法的参数当中。用法如下:
1.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param1")
public void simpleParam(String username,int age)
{
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(age);
}
|
访问该方法时,请求参数名和方法参数名相同,即可完成自动封装。
http://localhost:8080/c1/param1?username=bz&age=10
在SpringMVC中,接受简单类型参数时,请求参数名和方法参数名相同即可自动封装
SpringMVC参数获取_封装为对象类型

SpringMVC支持将参数直接封装为对象,写法如下:
封装单个对象
1.编写实体类
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
|
2.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param2")
public void objParam(Student student)
{
System.out.println(student);
}
|
3.访问该方法时,请求参数名和方法参数的属性名相同,即可完成自动封装。
http://localhost:8080/c1/param2?id=1&name=bz&sex=female
封装关联对象
1.编写实体类
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
public class Address {
private String info;
private String psotcode;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"info='" + info + '\'' +
", psotcode='" + psotcode + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
public String getPsotcode() {
return psotcode;
}
public void setPsotcode(String psotcode) {
this.psotcode = psotcode;
}
}
|
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Address address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
|
2.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param3")
public void objParam2(Student student)
{
System.out.println(student);
}
|
3.访问该方法时,请求参数名和方法参数的属性名相同,即可完成自动封装。
http://localhost:8080/c1/param3?id=1&name=bz&sex=female&address.info=beijing&address.postcode=030000
4.我们也可以使用表单发送带有参数的请求(直接访问jsp):
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>表单提交</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/c1/param3" method="post">
id:<input name="id">
姓名:<input name="name">
性别:<input name="sex">
地址:<input name="address.info">
邮编:<input name="address.postcode">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC参数获取_封装为集合类型
SpringMVC支持将参数封装为List或Map集合,写法如下:
封装为List集合
封装为简单数据类型集合
1.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param4")
public void listParam(@RequestParam List<String> users)
{
System.out.println(users);
}
|
该方法也可以绑定数组类型:
@RequestMapping("/c1/param5")
public void listParam2(@RequestParam String[] users){
System.out.println(users[0]);
System.out.println(users[1]);
}
|
2.请求的参数写法
http://localhost:8080/c1/param4?users=bj&users=sxt
封装为对象类型集合
SpringMVC不支持将参数封装为对象类型的List集合,但可以封装到有List属性的对象中
1.编写实体类
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
import java.util.List;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Address address;
private List<Address> addres;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", addres=" + addres +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public List<Address> getAddres() {
return addres;
}
public void setAddres(List<Address> addres) {
this.addres = addres;
}
}
|
2编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param6")
public void listParam3(Student student)
{
System.out.println(student);
}
|
3.请求的参数写法
http://localhost:8080/c1/param6?id=1&name=bz&sex=female&address[0\].info=bj&address[0].postcode=100010&address[1].info=sh&address[1].postcode=100011](http://localhost:8080/c1/param5?id=1&name=bz&sex=female&address[0].info=bj&address[0].postcode=100010&address[1].info=sh&address[1].postcode=100011)
封装为Map集合
同样,SpringMVC要封装Map集合,需要封装到有Map属性的对象中
1.编写实体类
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Map<String,Address> address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Map<String, Address> getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Map<String, Address> address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
|
2.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c1/param7")
public void mapParam(Student student)
{
System.out.println(student);
}
|
3.请求的参数写法
http://localhost:8080/c1/param7?id=1&name=bz&sex=female&address[‘one’\].info=bj&address[‘one’].postcode=100010&address[‘two’].info=sh&address[‘two’].postcode=100011]
SpringMVC参数获取_使用Servlet原生对象获取参数、

SpringMVC也支持使用Servlet原生对象,在方法参数中定义HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、HttpSession等类型的参数即可直接在方法中使用。
@RequestMapping("/c1/param8")
public void servletParam(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session)
{
System.out.println(request.getParameter("name"));
System.out.println(response.getCharacterEncoding());
System.out.println(session.getId());
}
|
访问该方法即可:http://localhost:8080/c1/param8?name=bjsxt
一般情况下,在SpringMVC中都有对Servlet原生对象的方法的替代,推荐使用SpringMVC的方式代替Servlet原生对象。
SpringMVC参数获取_自定义参数类型转换器

前端传来的参数全部为字符串类型,SpringMVC使用自带的转换器将字符串参数转为需要的类型。如:
@RequestMapping("/c1/param1")
public void simpleParam(String username,int age){
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(age);
}
|
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/c1/param1?username=bz&age=10
但在某些情况下,无法将字符串转为需要的类型,如:
@RequestMapping("/c1/param9")
public void dateParam(Date birthday){
System.out.println(birthday);
}
|
由于日期数据有很多种格式,SpringMVC没办法把所有格式的字符串转换成日期类型。比如参数格式为birthday=2025-01-01时,SpringMVC就无法解析参数。此时需要自定义参数类型转换器。
1.定义类型转换器类,实现Converter接口
package com.itbaizhan.converter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
@Override
public Date convert(String source) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = null;
try {
date = sdf.parse(source);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
}
|
2.注册类型转换器对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan"></context:component-scan>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="dateConverter"></mvc:annotation-driven>
<bean id="dateConverter" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.converter.DateConverter"></bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
|
SpringMVC参数获取_编码过滤器

在传递参数时,tomcat8以上能处理get请求的中文乱码,但不能处理post请求的中文乱码
1.编写jsp表单
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/18
Time: 22:35
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>编码过滤器</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/cn/code" method="post">
姓名:<input name="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
2.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/cn/code")
public void code(String username){
System.out.println(username);
}
|
SpringMVC提供了处理中文乱码的过滤器,在web.xml中配置该过滤器即可解决中文乱码问题:
3.web.xml配置文件加上过滤器
<filter>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
|
SpringMVC处理相应_配置视图解析器

SpringMVC默认情况下会在控制器执行完成后跳转到视图页面,视图解析器能找到相应的视图,之前的404异常就是由于没有配置视图解析器导致找不到视图。
在SpringMVC中提供了13个视图解析器,用于支持不同的视图技术。InternalResourceViewResolver是SpringMVC的默认视图解析器,用来解析JSP视图。
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
|
SpringMVC处理响应_控制器方法的返回值

我们可以通过控制器方法的返回值设置跳转的视图,控制器方法支持以下返回值类型:
返回值为void
此时会跳转到名字是 前缀+方法路径名+后缀 的jsp页面
1.编写控制器方法
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController2 {
@RequestMapping("/helloMVC")
public void helloMVC()
{
System.out.println("hello SpringMVC");
}
}
|
2.编写helloMVC.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/18
Time: 23:09
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>MVC</title>
</head>
<body>
<h11>欢迎来到MVC</h11>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC控制器方法返回值为void表示跳转到方法路径名的视图
返回值为String
此时会跳转到名字是前缀+返回值+后缀的jsp页面
编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("c2/hello1")
public String helloMVC1()
{
System.out.println("hello SpringMVC!");
return "helloMVC";
}
|
SpringMVC控制器方法返回值为String类型表示跳转到方法返回值的视图
返回值为ModelAndView
这是SpringMVC提供的对象,该对象可以向request域设置数据并指定跳转的页面。该对象中包含Model对象和View对象。
- Model:向request域中设置数据。
- View:指定跳转的页面。
1.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello2")
public ModelAndView useMAV()
{
System.out.println("返回值类型为ModelAndView");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
Map<String, Object> model = modelAndView.getModel();
model.put("name","百战程序员");
modelAndView.setViewName("baizhan");
return modelAndView;
}
|
2.编写jsp页面
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/18
Time: 23:41
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>百战</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>你好! ${requestScope.name}</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC处理响应_request域设置数据

当控制器返回值为ModelAndView时我们可以向request域设置数据,我们还有以下方法可以向request域设置数据:
使用原生的HttpServletRequest
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello3")
public String setRequestModel(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("username","尚学堂");
return "baizhan";
}
|
使用Model、ModelMap
SpringMVC提供了Model接口和ModelMap类,控制器方法添加这两个类型的参数,使用该参数设置数据,该数据就会存到request域中。
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello4")
public String setRequestModel2(Model model, ModelMap modelMap){
modelMap.addAttribute("username","尚学堂");
return "baizhan
|
使用Map集合
Model接口底层就是一个Map集合,我们可以给控制器方法设置Map类型的参数,向Map中添加键值对,数据也会存到request域中。
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello5")
public String setRequestModel3(Map map){
map.put("username","尚学堂");
return "baizhan";
}
|
SpringMVC处理响应_session域设置数据

Session作用域表示在当前会话中有效。在SpringMVC中对于Session作用域传值,只能使用HttpSession对象来实现。
1.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello6")
public String setSessionModel(HttpSession session)
{
session.setAttribute("address","北京");
return "baizhan";
}
|
2.编写jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java"
isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>百战</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>你好! ${requestScope.username}</h1>
<h1>地址是! ${sessionScope.address}</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC处理响应_context域设置数据
context作用域表示在整个应用范围都有效。在SpringMVC中对context作用域传值,只能使用ServletContext对象来实现。但是该对象不能直接注入到方法参数中,需要通过HttpSession对象获取。
1.编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello7")
public String setContextModel(HttpSession session)
{
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("age",10);
return "baizhan";
}
|
2.编写jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java"
isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>百战</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>你好! ${requestScope.username}</h1>
<h1>地址是! ${sessionScope.address}</h1>
<h1>年龄是! ${applicationScope.age}</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC处理响应_请求转发&重定向
之前的案例,我们发现request域中的值可以传到jsp页面中,也就是通过视图解析器跳转到视图的底层是请求转发。
如果我们跳转时不想使用视图解析器,可以使用原生HttpServletRequest进行请求转发或HttpServletResponse进行重定向:
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello8")
public void myForward1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{
request.setAttribute("name","尚学堂");
response.sendRedirect("/c2/hello9");
}
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello9")
public void myForward2(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println(request.getAttribute("name"));
}
|
SpringMVC还提供了一种更简单的请求转发和重定向的写法:
@RequestMapping("/c2/hello10")
public String myForward3(HttpServletRequest request)
{
request.setAttribute("name","尚学堂");
return "forward:/c2/hello9";
}
|
SpringMVC提供的重定向写法为: return "redirect:视图路径"
SpringMVC提供的请求转发写法为 return “forward:视图路径”
SpringMVC注解_@Controller
作用:标记控制器,将控制器交给Spring容器管理。
位置:类上方
SpringMVC注解_@RequestMapping
作用:给控制器方法设置请求路径
位置:方法或类上方。用于类上,表示类中的所有控制器方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
属性:
- value/path:请求路径
- method:指定请求方式
- params:规定必须发送的请求参数
- headers:规定请求必须包含的请求头
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c3")
public class MyController3 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/annotation1",method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST},params = {"age"},headers = {"User-agent"})
public String annotation1(String username){
System.out.println(username);
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
SpringMVC注解_@RequestParam
作用:在控制器方法中获取请求参数
位置:方法参数前
属性:
- name:指定请求参数名称
- defaultValue: 为参数设置默认值
- required:设置是否是必须要传入的参数
@RequestMapping("/annotation2")
public String annotation2(@RequestParam(name = "username",defaultValue = "sxt",required = false) String name){
System.out.println(name);
return "baizhan";
}
|
请求URL的写法:http://localhost:8080/c3/annotation2?username=bz

@RequestHeader
作用:在控制器方法中获取请求头数据
位置:方法参数前
@CookieValue
作用:在控制器方法中获取Cookie数据
位置:方法参数前
@RequestMapping("/annotation3")
public String annotation3(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent, @CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jSessionId){
System.out.println(userAgent);
System.out.println(jSessionId);
return "baizhan";
}
|
SpringMVC注解_@SessionAttributes

作用:将Model模型中的数据存到session域中
位置:类上方
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c4")
@SessionAttributes("name")
public class MyController4 {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String t1(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","北京尚学堂");
return "baizhan";
}
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String t2(HttpSession session){
System.out.println(session.getAttribute("name"));
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
在SpringMVC中,可以将Model模型中的数据存到session域中@SessionAttributes
SpringMVC注解_@ModelAttribute
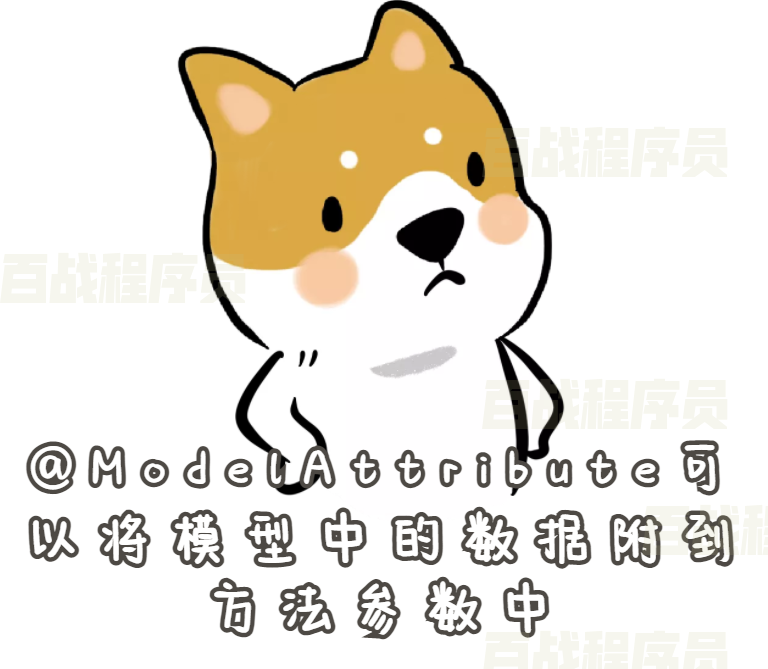
作用1:设置指定方法在控制器其他方法前执行
位置:方法上方
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c5")
public class MyController5 {
@ModelAttribute
public void before(){
System.out.println("前置方法");
}
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String t1(){
System.out.println("t1");
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
作用2:从Model模型中获取数据给参数赋值
位置:方法参数前
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c6")
public class MyController6 {
@ModelAttribute
public void before(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","尚学堂");
}
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String t1(@ModelAttribute("name") String name){
System.out.println(name);
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
SpringMVC注解_RESTful风格支持

RESTful风格介绍
RESTful风格是一种URL路径的设计风格。在RESTful风格的URL路径中,网络上的任意数据都可以看成一个资源,它可以是一段文本、一张图片,也可以是一个Java对象。而每个资源都会占据一个网络路径,无论对该资源进行增删改查,访问的路径是一致的。
传统URL:
RESTful风格URL:
那么如何区分对该资源是哪一种操作?通过请求方式不同,判断进行的是什么操作。之前我们学过两种请求方式,GET请求和POST请求,而访问RESTful风格的URL一共有四种请求方式:
- GET请求:查询操作
- POST请求:新增操作
- DELETE请求:删除操作
- PUT请求:修改操作
RESTful风格URL:
RESTful风格的特点:
结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、拓展方便
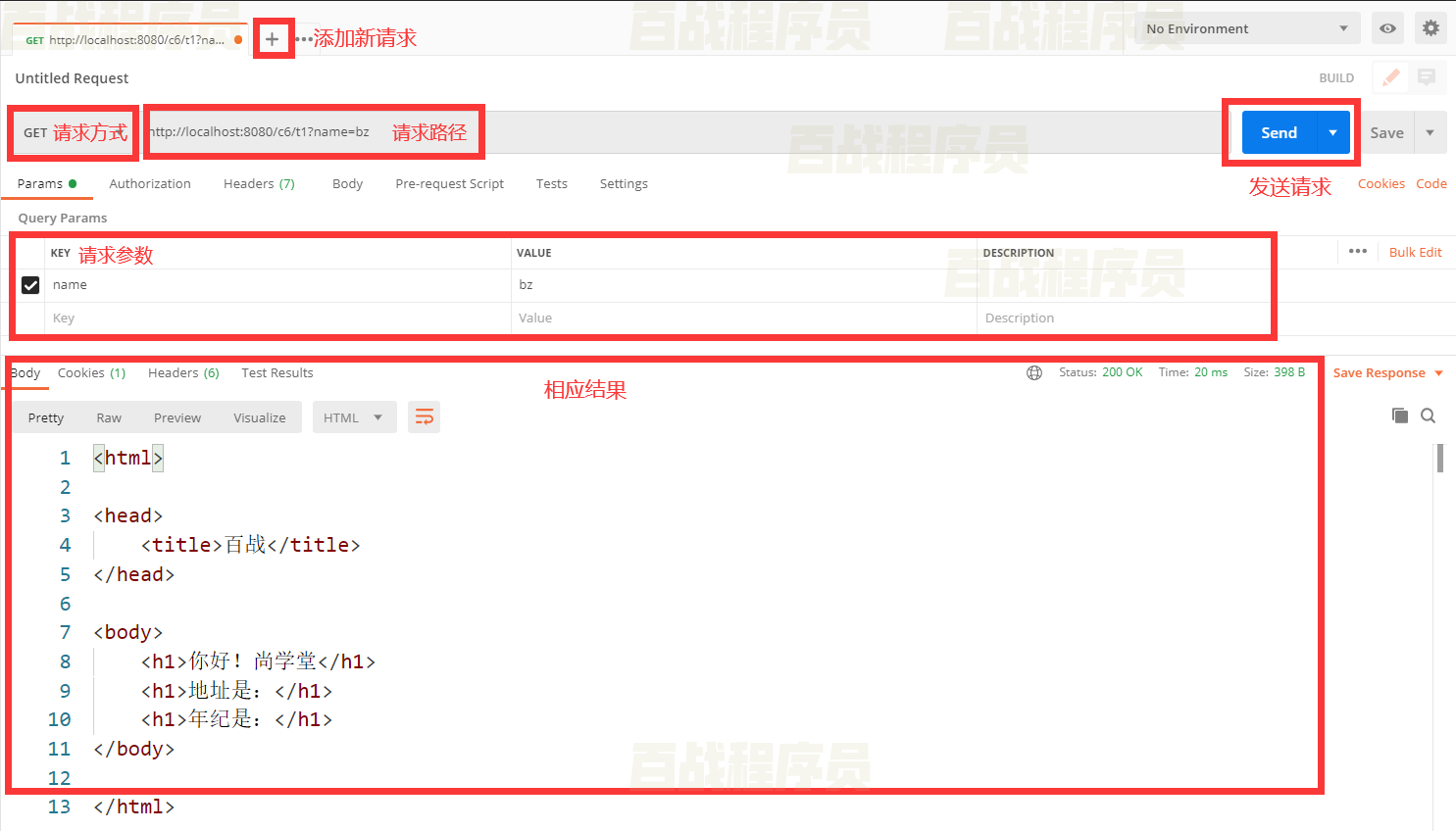
POSTMAN使用
默认情况下浏览器是无法发送DELETE请求和PUT请求的,我们可以使用Postman工具发送这些请求。
双击安装包安装Postman
点击new-collection创建请求集合
3.添加请求
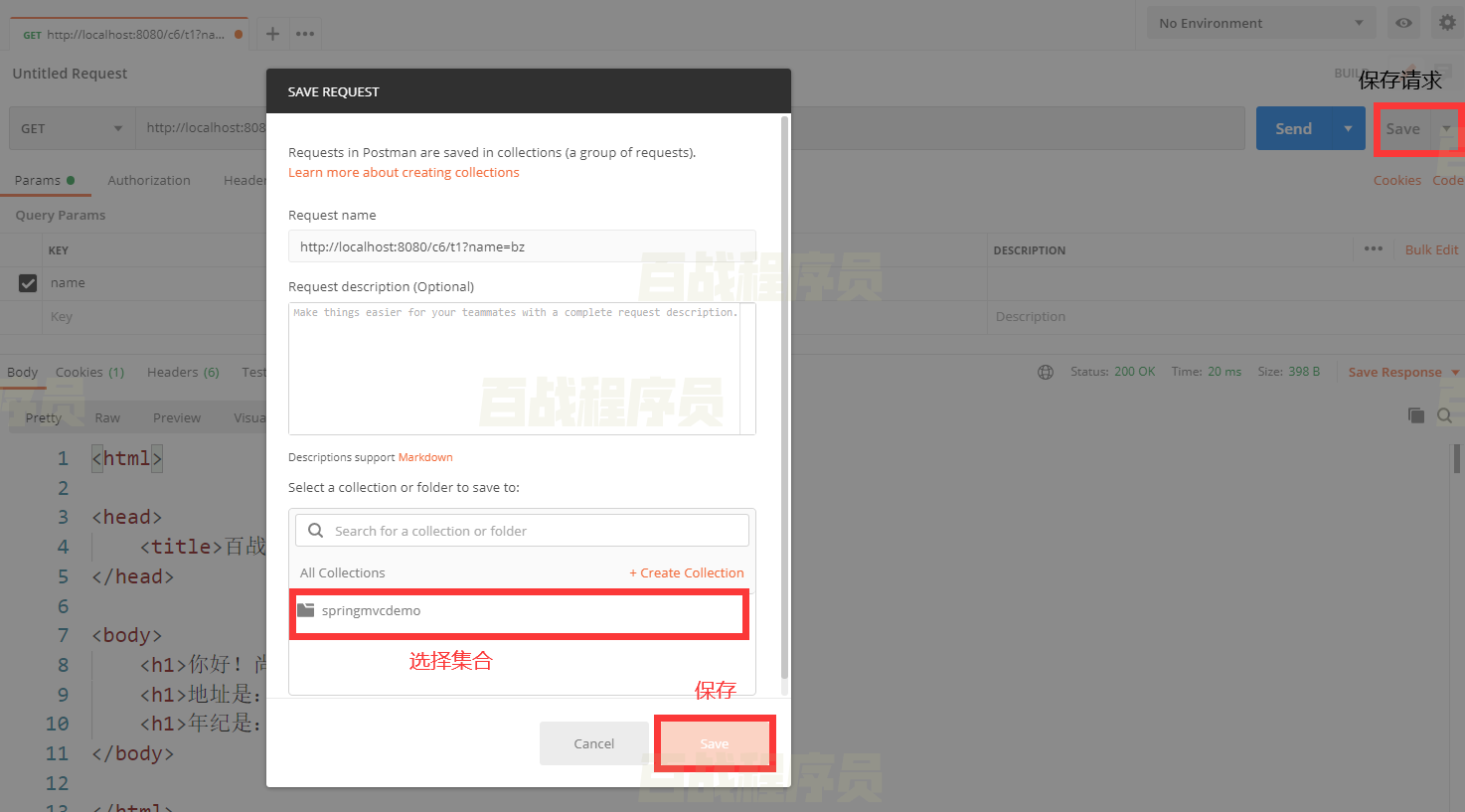
4.保存请求到集合,以后可以随时发送该请求
@PathVariable

作用:在RESTful风格的URL中获取占位符的值
位置:方法参数前
属性:
- value:获取哪个占位符的值作为参数值,如果占位符和参数名相同,可以省略该属性。
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import com.itbaizhan.domain.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id)
{
System.out.println("删除id为"+id+"的学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println("新增学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String findStudentById(@PathVariable int id)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println("根据id查询学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println("修改学生");
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
访问方式:
@PostMapping、@GetMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping
作用:简化设置请求方式的@RequestMapping写法
位置:方法上方。
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import com.itbaizhan.domain.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id)
{
System.out.println("删除id为"+id+"的学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@PostMapping("/{id}")
public String addStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println("新增学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String findStudentById(@PathVariable int id)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println("根据id查询学生");
return "baizhan";
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public String updateStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student)
{
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println("修改学生");
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
HiddentHttpMethodFilter

由于浏览器form表单只支持GET与POST请求,而DELETE、PUT请求并不支持,SpringMVC有一个过滤器,可以将浏览器的POST请求改为指定的请求方式,发送给的控制器方法。
用法如下:
1.在web.xml中配置过滤器
<filter>
<filter-name>httpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>httpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
|
2.编写控制器方法
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c7")
public class MyController7
{
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public String testDelete()
{
System.out.println("删除方法");
return "baizhan";
}
@PutMapping("/put")
public String testPut()
{
System.out.println("修改方法");
return "baizhan";
}
}
|
3.在jsp中编写表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>DELETE、PUT提交</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--删除--%>
<%-- 提交DELETE、PUT请求,表单必须提交方式为post --%>
<form action="/c7/delete" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
<input type="submit" value="删除">
</form>
<hr/>
<%-- 修改 --%>
<form action="/c7/put" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<input type="submit" value="修改">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC注解_@ResponseBody

作用:方法返回的对象转换为JSON格式,并将JSON数据直接写入到输出流中,使用此注解后不会再经过视图解析器。使用该注解可以处理Ajax请求。
位置:方法上方或方法返回值前
1.编写jsp页面,发送ajax请求
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>ajax请求 </title>
<script src="/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
var name =$("#name").val();
var sex =$("#sex").val();
$.get("/c8/addStudent",{"name":name,"sex":sex},function (data) {
console.log(data);
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
姓名:<input id="name"/><br/>
性别:<input id="sex"/><br/>
<input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"/>
</body>
</html>
|
2.由于jsp页面中引入jQuery的js文件,而SpringMVC会拦截所有资源,造成jquery.js失效,需要在SpringMVC核心配置文件中放行静态资源。
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
|
3.编写结果实体类,该实体类会封装一个请求的结果
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
public class Result {
private boolean flag;
private String message;
public Result() {
}
public Result(boolean flag, String message) {
this.flag = flag;
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Result{" +
"flag=" + flag +
", message='" + message + '\'' +
'}';
}
public boolean isFlag() {
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
|
4.编写控制器
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import com.itbaizhan.domain.Result;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c8")
public class MyController8 {
@PostMapping("/addStudent")
@ResponseBody
public Result addStudent(String name,String sex)
{
System.out.println(name+":"+sex);
Result result = new Result(true, "添加学生成功!");
return result;
}
}
|
5.SpringMVC会将Result对象转为JSON格式写入输出流,而SpringMVC默认使用的JSON转换器是jackson,需要在pom中添加jackson依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
|
SpringMVC注解_@RestController
如果一个控制器类下的所有控制器方法都返回JSON格式数据且不进行跳转,可以使用@RestController代替@Controller,此时每个方法上的@ResonseBody都可以省略
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/c8")
public class MyController8 {
@PostMapping("/addStudent")
public Result addStudent(String name,String sex)
{
System.out.println(name+":"+sex);
Result result = new Result(true, "添加学生成功!");
return result;
}
}
|
静态资源映射

当在DispatcherServlet的中配置拦截”/“时,除了jsp文件不会拦截以外,其他所有的请求都会经过前端控制器进行匹配。此时静态资源例如css、js、jpg等就会被前端控制器拦截,导致不能访问,出现404问题。想要正常映射静态资源共有三种方案:
配置静态资源筛查器
在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置<mvc:default-servlet-handler />后,会在Spring容器中创建一个资源检查器,它对进入DispatcherServlet的URL进行筛查,如果不是静态资源,才由DispatcherServlet处理。
修改SpringMVC核心配置文件:
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
|
配置静态资源映射器
SpringMVC模块提供了静态资源映射器组件,通过<mvc:resources>标签配置静态资源映射器,配置后的路径不会由DispatcherServlet处理。
修改SpringMVC核心配置文件:
<mvc:resources mapping="/img/" location="/img/"/><mvc:resources mapping="/js/" location="/js/"/>
|
配置默认Servlet处理静态资源
在web.xml可以配置默认Servlet处理静态资源,该Servlet由tomcat提供,它会直接访问静态资源不进行其他操作。这样就避免了使用DispatcherServlet对静态资源的拦截:
修改web.xml:
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jpg</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.css</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.js</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.png</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
SpringMVC注解_@RequestBody

作用:将请求中JSON格式的参数转为JAVA对象
位置:写在方法参数前
1.AJAX请求发送JSON格式的参数
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>ajax请求 </title>
<script src="/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
var name =$("#name").val();
var sex =$("#sex").val();
var param = JSON.stringify({"name":name,"sex":sex});
$.ajax({
url:"/c8/addStudent2",
contentType:"application/json",
type:"post",
data:param,
success:function (data) {
console.log(data);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
姓名:<input id="name"/><br/>
性别:<input id="sex"/><br/>
<input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"/>
</body>
</html>
|
2.编写控制器
@PostMapping("/addStudent2")
public Result addStudent(@RequestBody Student student)
{
System.out.println(student);
Result result = new Result(true, "添加学生成功!");
return result;
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_原生方式上传

上传是Web工程中很常见的功能,SpringMVC框架简化了文件上传的代码,我们首先使用JAVAEE原生方式上传文件:
1.创建新的SpringMVC项目,在web.xml中将项目从2.3改为3.1,即可默认开启el表达式
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1">
|
2.编写上传表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件上传</h3>
<%--上传表单的提交方式必须是post--%>
<%-- enctype属性为multipart/form-data,意思是不对表单数据进行编码 --%>
<form action="/fileUpload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<%-- 文件选择控件,类型是file,必须要有name属性--%>
选择文件:<input type="file" name="upload"/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
3.接受请求体数据:
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload")
public String upload(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
ServletInputStream is = request.getInputStream();
int i = 0;
while ((i=is.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}
return "index";
}
|
接下来需要分析请求体中的文件项,并将数据写入磁盘,此时需要借助文件上传工具
1.引入文件上传依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
</dependency>
|
2.编写控制器接收上传请求,控制器进行三步操作
- 创建文件夹,存放上传文件。
- 分析请求体,找到上传文件数据。
- 将文件数据写入文件夹。
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.ServletInputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UploadController {
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload")
public String upload(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File file = new File(realPath);
if(!file.exists())
{
file.mkdirs();
}
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
ServletFileUpload servletFileUpload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
List<FileItem> fileItems = servletFileUpload.parseRequest(request);
for (FileItem fileItem : fileItems) {
if(!fileItem.isFormField())
{
String name = fileItem.getName();
fileItem.write(new File(file,name));
fileItem.delete();
}
}
return "index";
}
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_SpringMVC方式上传

SpringMVC使用框架提供的文件解析器对象,可以直接将请求体中的文件数据转为MultipartFile对象,从而省略原生上传中分析请求体的步骤。
1.在SpringMVC核心配置文件配置文件解析器
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="104857600"></property>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="utf-8"></property>
</bean>
|
2.创建JSP表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件上传</h3>
<%--上传表单的提交方式必须是post--%>
<%-- enctype属性为multipart/form-data,意思是不对表单数据进行编码 --%>
<form action="/fileUpload2" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<%-- 文件选择控件,类型是file,必须要有name属性--%>
选择文件:<input type="file" name="file"/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
3.编写控制器接受上传请求
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload2")
public String upload2(MultipartFile file,HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File dir = new File(realPath);
if(!dir.exists())
{
dir.mkdirs();
}
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
originalFilename = UUID.randomUUID()+"_"+originalFilename;
File newFile = new File(dir,originalFilename);
file.transferTo(newFile);
return "index";
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_上传多文件
SpringMVC支持一次性上传多个文件,写法如下:
1.创建JSP表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件上传</h3>
<%--上传表单的提交方式必须是post--%>
<%-- enctype属性为multipart/form-data,意思是不对表单数据进行编码 --%>
<form action="/fileUpload3" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<%-- 文件选择控件,类型是file,必须要有name属性--%>
用户名:<input name="username"><br/>
文件1:<input type="file" name="files"/><br/>
文件2:<input type="file" name="files"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
2.编写控制器接收上传请求
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload3")
public String upload3(MultipartFile files[],String username,HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
System.out.println(username);
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File dir = new File(realPath);
if (!dir.exists()){
dir.mkdirs();
}
for(MultipartFile file:files)
{
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
originalFilename = UUID.randomUUID()+"_"+originalFilename;
File newFile = new File(dir, originalFilename);
file.transferTo(newFile);
}
return "index";
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_异步上传
之前的上传答案,在上传成功后都会跳转页面。而在实际开发中,很多情况下上传后不进行跳转,而是进行页面的局部刷新,比如:上传头像成功后将头像显示在网页中。这时候就需要使用异步文件上传。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>上传</title>
<script src = "/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/js/jquery.form.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件上传</h3>
<%--上传表单的提交方式必须是post--%>
<%-- enctype属性为multipart/form-data,意思是不对表单数据进行编码 --%>
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" id="ajaxForm">
图片上传:<input type="file" name="file"/>
<%-- 按钮类型不能是submit,否则会刷新页面 --%>
<input type="button" value="上传头像" id="btn"/>
</form>
<%--上传头像后展示的位置--%>
<img src="/" width="100" id="img">
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
$("#ajaxForm").ajaxSubmit(
{
url:"/fileUpload4",
type:"post",
success:function (data) {
$("#img").attr("src",data);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
2.编写控制器接收异步上传请求
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload4")
@ResponseBody
public String upload4(MultipartFile file,HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File dir = new File(realPath);
if(!dir.exists())
{
dir.mkdirs();
}
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
originalFilename = UUID.randomUUID()+"_"+originalFilename;
File newFile = new File(dir,originalFilename);
file.transferTo(newFile);
return "/upload/"+originalFilename;
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_跨服务器上传
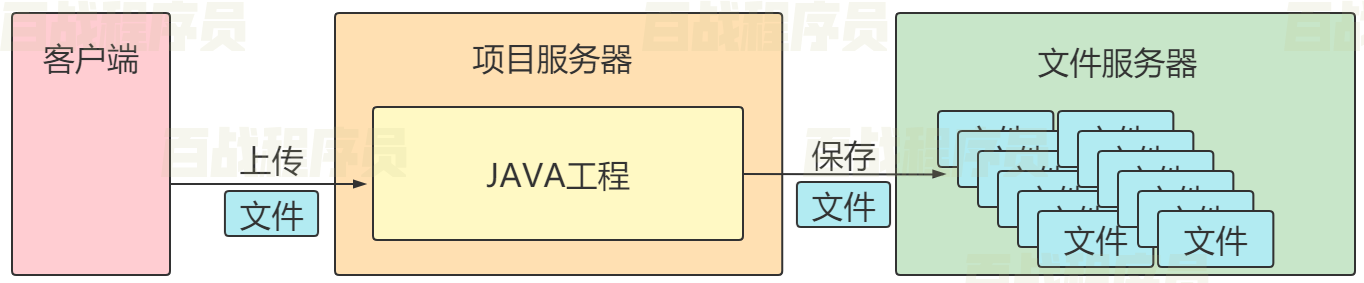
由于文件占据磁盘空间较大,在实际开发中往往会将文件上传到其他服务器中,此时需要使用跨服务器上传文件。
1.在tomcat的webapps下创建upload目录作为文件上传目录。
2.修改tomcat的conf/web.xml文件,支持跨服上传
<servlet>
<init-param>
<param-name>readonly</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
|
3.修改tomcat的conf/server.xml文件,修改tomcat端口,修改完开启tomcat服务器
<Connector port="8081" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" />
|
4.编写JSP上传表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>上传</title>
<script src = "/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/js/jquery.form.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件上传</h3>
<%--上传表单的提交方式必须是post--%>
<%-- enctype属性为multipart/form-data,意思是不对表单数据进行编码 --%>
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" id="ajaxForm">
图片上传:<input type="file" name="file"/>
<%-- 按钮类型不能是submit,否则会刷新页面 --%>
<input type="button" value="上传头像" id="btn"/>
</form>
<%--上传头像后展示的位置--%>
<img src="/" width="100" id="img">
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
$("#ajaxForm").ajaxSubmit(
{
url:"/fileUpload5",
type:"post",
success:function (data) {
$("#img").attr("src",data);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
5.添加跨服上传依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-core</artifactId>
<version>1.18.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-client</artifactId>
<version>1.18.1</version>
</dependency>
|
6.创建控制器方法,该方法在接受到上传请求后将文件保存到其他服务器上。
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload5")
@ResponseBody
public String upload4(HttpServletRequest request, MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
String path = "http://localhost:8888/upload/";
String filename = file.getOriginalFilename();
filename = UUID.randomUUID()+"_"+filename;
Client client = Client.create();
WebResource resource = client.resource(path + filename);
resource.put(file.getBytes());
return path+filename;
}
|
SpringMVC文件上传_文件下载
将文件上传到服务器后,有时我们需要让用户下载上传的文件,接下来我们编写文件下载功能:
查询所有可下载的文件
1.编写控制器方法,查询所有可下载的文件,并跳转到下载页面
@Controller
public class DownLoadController {
@RequestMapping("/showFiles")
public String showFileDown(HttpServletRequest request, Model model)
{
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File file = new File(realPath);
String[] files = file.list();
model.addAttribute("files",files);
return "download";
}
|
2.添加JSTL依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>taglibs-standard-spec</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>taglibs-standard-impl</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
</dependency>
|
3.编写下载页面
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/20
Time: 20:40
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>下载</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>文件下载</h3>
<%--遍历文件集合--%>
<c:forEach items="${files}" var="file">
<a href="/download?fileName=${file}">${file}</a><br/>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
|
编写下载控制器
@RequestMapping("/download")
public void fileDown(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,String fileName) throws IOException {
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+fileName);
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File file = new File(path,fileName);
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
os.write(FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file));
os.flush();
os.close();
}
|
SpringMVC异常处理_单个控制器异常处理

在系统当中, Dao、Service、Controller层代码出现都可能抛出异常。如果哪里产生异常就在哪里处理,则会降低开发效率。所以一般情况下我们会让异常向上抛出,最终到达DispatcherServlet中,此时SpringMVC提供了异常处理器进行异常处理,这样可以提高开发效率。
处理单个控制器的异常:
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String t1()
{
String str = null;
int[] arr = new int[1];
arr[2] = 10;
return "index";
}
@ExceptionHandler({java.lang.NullPointerException.class,java.lang.ArithmeticException.class})
public String exceptionHandler1(Exception ex, Model model)
{
model.addAttribute("msg",ex);
return "error";
}
@ExceptionHandler({java.lang.Exception.class})
public String exceptionHandler2(Exception ex, Model model)
{
model.addAttribute("msg",ex);
return "error2";
}
}
|
异常页面error.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/20
Time: 21:16
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>出错了!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>ERROR!!! 发生异常 ${msg}</h3>
</body>
</html>
|
异常页面error2.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>出错了!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>ERROR2 发生严重异常!${msg}</h3>
</body>
</html>
|
SpringMVC异常处理_全局异常处理

在控制器中定义异常处理方法只能处理该控制器类的异常,要想处理所有控制器的异常,需要定义全局异常处理类。
1.编写另一个有异常的控制器类
@Controller
public class MyController2 {
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String t2(){
int[] arr = new int[1];
arr[2] = 10;
return "index";
}
}
|
2.编写全局异常处理器类
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler({java.lang.NullPointerException.class,java.lang.ArithmeticException.class})
public String exceptionHandler1(Exception ex, Model model)
{
model.addAttribute("msg",ex);
return "error";
}
@ExceptionHandler({java.lang.Exception.class})
public String exceptionHandler2(Exception ex, Model model)
{
model.addAttribute("msg",ex);
return "error2";
}
}
|
SpringMVC异常处理_自定义异常处理器

以上方式都是使用的SpringMVC自带的异常处理器进行异常处理,我们还可以自定义异常处理器处理异常:
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Component
public class MyExceptionHandler implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
if(e instanceof NullPointerException)
{
modelAndView.setViewName("error");
}else
{
modelAndView.setViewName("error2");
}
modelAndView.addObject("msg",e);
return modelAndView;
}
}
|
SpringMVC拦截器_拦截器简介
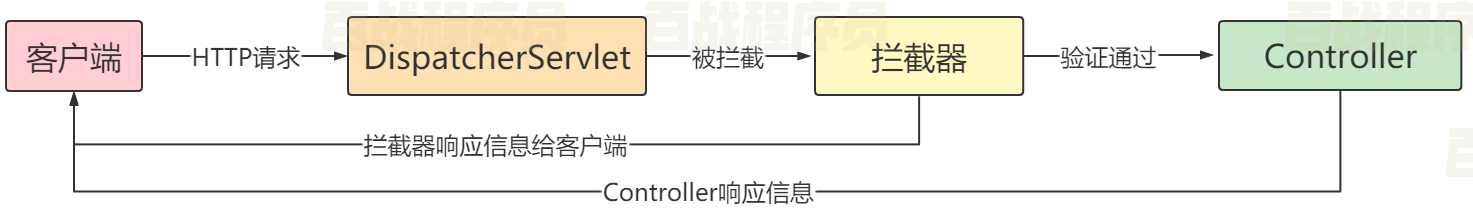
SpringMVC的拦截器(Interceptor)也是AOP思想的一种实现方式。它与Servlet的过滤器(Filter)功能类似
主要用于拦截用户的请求并做相应的处理,通常应用在权限验证、记录请求信息的日志、判断用户是否登录等功能上。
拦截器和过滤器的区别
- 拦截器是SpringMVC组件,而过滤器是Servlet组件。
- 拦截器不依赖Web容器,过滤器依赖Web容器。
- 拦截器只能对控制器请求起作用,而过滤器则可以对所有的请求起作用。
- 拦截器可以直接获取IOC容器中的对象,而过滤器就不太方便获取。
SpringMVC拦截器_拦截器使用
1.使用maven创建SpringMVC的web项目
2.创建控制器方法
package com.itbaizhan.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController1 {
@RequestMapping("/m1")
public String m1()
{
System.out.println("控制器方法");
return "result";
}
}
|
3.创建拦截器类,该类实现HandlerInterceptor接口,需要重写三个方法:
- preHandle:请求到达Controller前执行的方法,返回值为true通过拦截器,返回值为false被拦截器拦截。
- postHandle:跳转到JSP前执行的方法
- afterCompletion:跳转到JSP后执行的方法
package com.itbaizhan.interceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("请求到达Controller前");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("跳转到JSP前");
request.setAttribute("name","百战");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("跳转到JSP后");
request.setAttribute("age",10);
}
}
|
4.编写JSP页面
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 百里诀
Date: 2022/4/20
Time: 23:13
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>结果</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>name:${requestScope.name}</h3>
<h3>age:${requestScope.age}</h3>
</body>
</html>
|
5.在SpringMVC核心配置文件中配置拦截器
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.interceptor.MyInterceptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
|
SpringMVC拦截器_全局拦截器
全局拦截器可以拦截所有控制器处理的URL,作用等于/**,配置方式如下:
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.interceptor.MyInterceptor">
</bean>
</mvc:interceptors>
|
SpringMVC拦截器_拦截器链与执行顺序
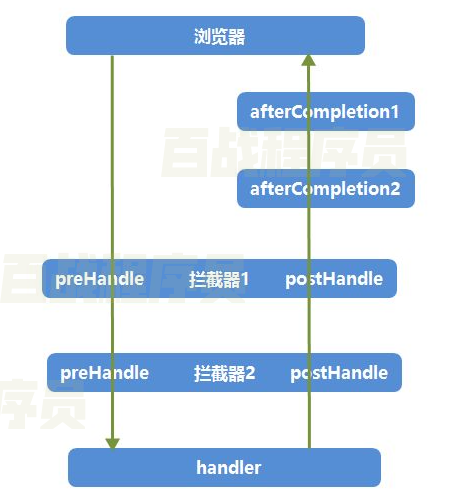
如果一个URL能够被多个拦截器所拦截,全局拦截器最先执行,其他拦截器根据配置文件中配置的从上到下执行,接下来我们再配置一个拦截器:
1.编写拦截器类
package com.itbaizhan.interceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class MyInterceptor2 implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器2:请求到达Controller前");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器2:跳转到JSP前");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器2:跳转到JSP后");
}
}
|
2.配置拦截器链(在springmvc.xml配置)
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.interceptor.MyInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.interceptor.MyInterceptor2"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
|
访问控制器方法后输出如下:

结论:
- preHandle()顺序执行,postHandle()、afterComletion()逆序执行。
- 只要有一个preHandle()拦截,后面的preHandle(),postHandle()都不会执行。
- 只要相应的preHandle()放行,afterComletion()就会执行。
SpringMVC跨域请求_同源策略

同源策略是浏览器的一个安全功能。同源,指的是两个URL的协议,域名,端口相同。浏览器出于安全方面的考虑,不同源的客户端脚本在没有明确授权的情况下,不能读写对方资源。
哪些不受同源策略限制:
- 页面中的
<a>跳转、表单提交不会受到同源策略限制的。
- 静态资源引入也不会受到同源策略限制。如嵌入到页面中的
<script src="">,<img src="">,<link href="">等。
- 最容易收到同源策略影响的就是Ajax请求。
SpringMVC跨域请求_跨域请求

当请求URL的协议、域名、端口三者中任意一个与当前页面URL不同时即为跨域。浏览器执行JavaScript脚本时,会检查当前请求是否同源,如果不是同源资源,就不会被执行。
1.编写控制器方法
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class MyController3 {
@RequestMapping("/m3")
public String m3(Model model)
{
System.out.println("测试跨域请求");
return "success";
}
|
2.编写JSP页面,发送异步请求
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>跨域请求</title>
<script src="/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
$.get("http://127.0.0.1:8080/m3", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">异步请求</button>
</body>
</html>
|
结果:
当浏览器通过http://localhost:8080/cross.jsp访问JSP页面时

SpringMVC跨域请求_控制器接收跨域请求

SpringMVC提供了注解@CrossOrigin解决跨域问题。用法如下:
@RequestMapping("/m3")
@ResponseBody
@CrossOrigin("http://localhost:8080")
public String m3(){
System.out.println("测试跨域请求");
return "success";
}
|
SSM整合_需求分析
接下来我们使用Maven+Spring+MyBatis+SpringMVC完成一个案例,案例需求为在页面可以进行添加学生+查询所有学生!
案例需要使用以下技术:
- 使用Maven创建聚合工程,并使用Maven的tomcat插件运行工程
- 使用Spring的IOC容器管理对象
- 使用MyBatis操作数据库
- 使用Spring的声明式事务进行事务管理
- 使用SpringMVC作为控制器封装Model并跳转到JSP页面展示数据
- 使用Junit测试方法
- 使用Log4j在控制台打印日志
案例的编写流程如下:
- 创建maven父工程,添加需要的依赖和插件
- 创建dao子工程,配置MyBatis操作数据库,配置Log4j在控制台打印日志。
- 创建service子工程,配置Spring声明式事务
- 创建controller子工程,配置SpringMVC作为控制器,编写JSP页面展示数据。
- 每个子工程都使用Spring进行IOC管理
# 准备数据库数据
CREATE DATABASE `student`;
USE `student`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` VARCHAR(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `student`(`id`,`name`,`sex`,`address`) VALUES (1,'百战程序员','男','北京'),(2,'北京尚学堂','女','北京');
|
SSM整合_创建父工程
创建maven父工程,添加需要的依赖和插件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm_demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<spring.version>5.2.12.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>taglibs-standard-spec</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>taglibs-standard-impl</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>8080</port>
<path>/</path>
<uriEncoding>UTF-8</uriEncoding>
<server>tomcat7</server>
<systemProperties>
<java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format>%1$tH:%1$tM:%1$tS %2$s%n%4$s: %5$s%6$s%n
</java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format>
</systemProperties>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
SSM整合_创建dao子工程
1.在父工程下创建maven普通java子工程
2.编写实体类
package com.itbaizhan.domain;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, String sex, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.address = address;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
|
3.编写持久层接口
package com.itbaizhan.dao;
import com.itbaizhan.domain.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface StudentDao {
@Select("select * from stduent")
List<Student> findAll();
@Insert("insert into student values(null.#{name},#{sex},#{address})")
void add(Student student);
}
|
4.编写log4j.properties配置文件
log4j.rootCategory=debug, CONSOLE, LOGFILE
log4j.logger.org.apache.axis.enterprise=FATAL, CONSOLE
log4j.appender.CONSOLE=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout.ConversionPattern=[%d{MM/dd HH:mm:ss}] %-6r [%15.15t] %-5p %30.30c %x - %m\n
|
5.编写数据库配置文件druid.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///student
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
|
6.编写MyBatis配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration>
|
7.编写Spring配置文件applicationContext-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:druid.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="dataSouce" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSouce"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:SqlMapConfig.xml"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itbaizhan.dao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
|
8.测试持久层接口的方法
package com.itbaizhan.dao;
import com.itbaizhan.domain.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext-dao.xml")
public class StudentDaoTest {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Test
public void testFindAll()
{
List<Student> all = studentDao.findAll();
for (Student student : all) {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}
@Test
public void testAdd(){
Student student = new Student(0, "wwww", "ewg", "fsf");
studentDao.add(student);
}
}
|
SSM整合_创建service子工程
在父工程下创建maven普通java子工程
service子工程引入dao子工程的依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm_dao</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
3.创建服务层方法
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
public List<Student> findAllStudent(){
return studentDao.findAll();
}
public void addStudent(Student student){
studentDao.add(student);
}
}
|
4.创建服务层的Spring配置文件applicationContext-service.xml,配置声明式事务
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan.service"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.itbaizhan.service.*.*(..))"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>
|
SSM整合_创建controller子工程
1.在父工程下使用maven创建web类型子工程
2.controller工程引入service子工程的依赖,并配置ssm父工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm_controller</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<parent>
<artifactId>ssm_demo</artifactId>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itbaizhan</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm_service</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
|
3.编写控制器类
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/all")
public String all(Model model)
{
List<Student> allStudent = studentService.findAllStudent();
model.addAttribute("students",allStudent);
return "allStudent";
}
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(Student student)
{
studentService.addStudent(student);
return "redirect:/student/all";
}
}
|
4.编写SpringMVC配置文件springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan.controller"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
</beans>
|
5.编写Spring的总配置文件applicationContext.xml,该文件引入dao和service层的Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="applicationContext-dao.xml"></import>
<import resource="applicationContext-service.xml"></import>
</beans>
|
6.在web.xml中配置Spring监听器,该监听器会监听服务器启动,并自动创建Spring的IOC容器
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
|
7.在web.xml中配置SpringMVC的前端控制器和编码过滤器
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
|
8.编写JSP页面allStudent.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>所有学生</title>
</head>
<body>
<%-- 添加学生表单 --%>
<form action="/student/add" method="post">
姓名:<input name="name">
性别:<input name="sex">
地址:<input name="address">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<%-- 展示学生表格 --%>
<table width="500" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="center">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>地址</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="#{students}" var="student">
<tr>
<td>${student.id}</td>
<td>${student.name}</td>
<td>${student.sex}</td>
<td>${student.address}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
|











































